The Balanced Scorecard is a powerful strategy framework that goes beyond just understanding its principles; it’s about effective execution. Successful implementation of the Balanced Scorecard requires a well-thought-out business strategy that addresses both the ‘HOW’ and the ‘WHAT’ aspects of the framework.
In this article, we will delve into the steps needed to implement the Balanced Scorecard framework and explore its various perspectives and benefits.
What is a Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard, introduced by Robert Kaplan and David P. Norton in the 1990s, is a widely acclaimed strategy management system that helps align strategic initiatives and operational objectives to improve business performance. It focuses on creating Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) across four critical areas, enabling informed decision-making.
Studies have shown the widespread adoption of the Balanced Scorecard by U.S. companies since the late 1990s, indicating its intuitive appeal. The framework guides organizations towards four perspectives, emphasizing both leading and lagging KPIs and a balanced approach to short-term and long-term goals.
Four Perspectives of a Balanced Scorecard
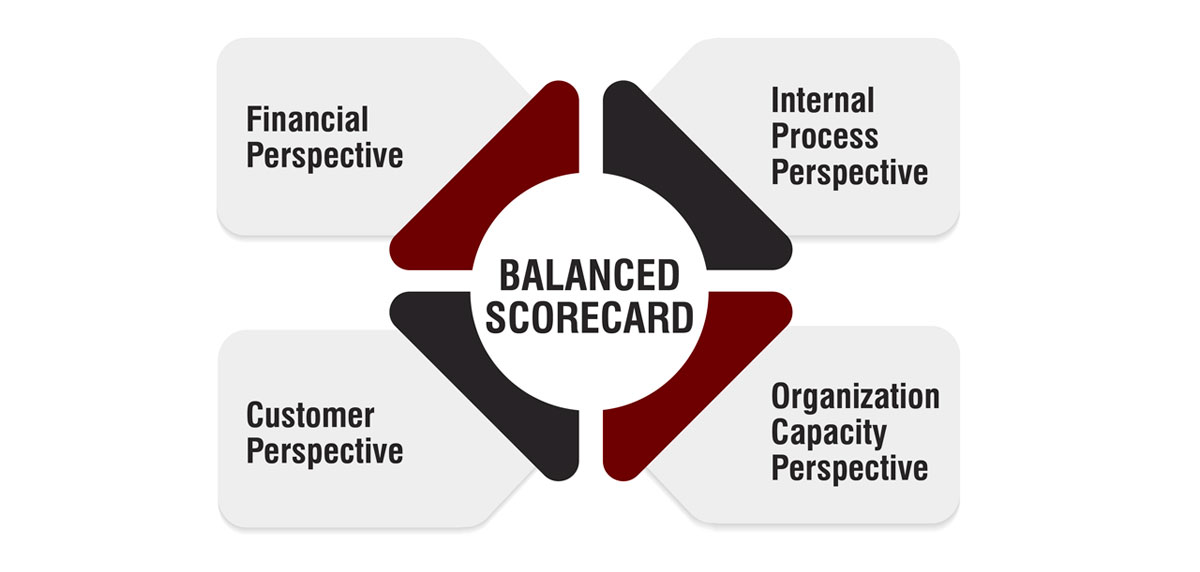
- Financial Perspective: Focuses on evaluating the financial health and performance of the enterprise, including metrics like revenue growth, operating income, and return on equity.
- Customer Perspective: Compares the enterprise’s service offerings with competitors from a customer viewpoint, measuring metrics such as customer satisfaction and retention.
- Internal Process Perspective: Evaluates the efficiency and effectiveness of internal business processes, tracking metrics like order processing time and cycle time.
- Organization Capacity Perspective: Acknowledges the importance of human capital and organizational capabilities in driving improvement, monitoring metrics like employee satisfaction and training investments.
These perspectives collectively provide a holistic assessment of an organization’s performance and alignment with strategic objectives.
Benefits of Building a Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard is a versatile tool used across various sectors to measure internal performance based on financial, customer, internal process, and organizational capacity perspectives. Its simplicity and applicability to different types of organizations make it a valuable asset for strategic management.
Implementing a Balanced Scorecard offers several advantages, including a focus on key success factors, effective communication of strategy, identification of competitive advantages, and enhanced accountability among employees.
Steps to Implement a Balanced Scorecard with Example
Here’s a guide on how business strategists can implement a Balanced Scorecard:
- Define Clear Objectives: Understand organizational goals aligned with the mission and strategy, such as improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Choose Relevant KPIs: Select KPIs that align with objectives, like waste reduction percentage and customer satisfaction index.
- Develop Action Plans: Create strategic plans to achieve KPIs, such as implementing lean manufacturing techniques and enhancing quality control processes.
- Align the Organization: Organize resources to support the Balanced Scorecard, aligning employee roles with specific KPIs.
- Communicate Effectively: Ensure stakeholders understand the Balanced Scorecard and their role in achieving objectives.
- Regular Review and Revision: Periodically review the effectiveness of the Balanced Scorecard and adjust objectives based on success or organizational needs.
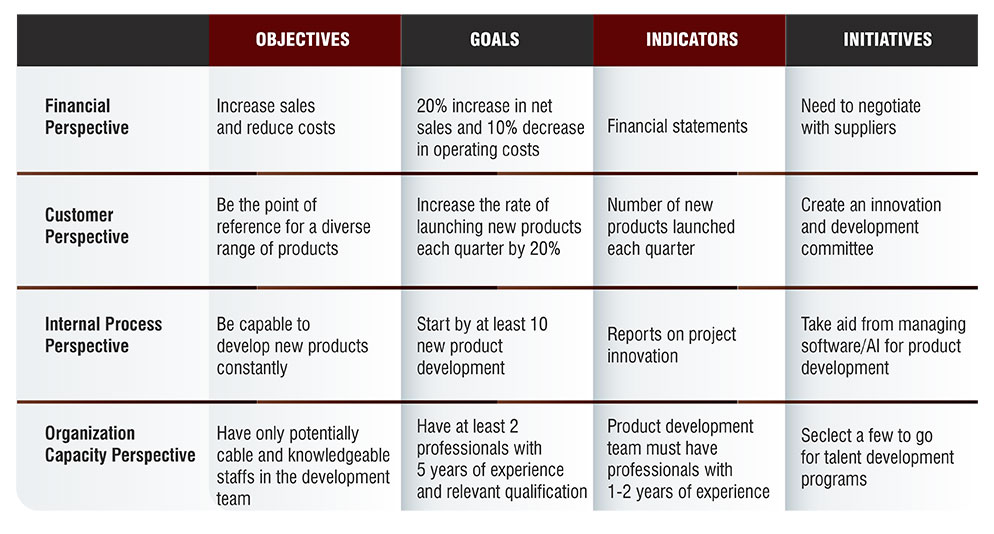
Balanced Scorecard Example: Strategic map for an E-Commerce Business
Conclusion
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard requires a strategic approach to translate an organization’s vision into operational objectives. By balancing financial metrics with internal processes, customer perspectives, and organizational growth, businesses can achieve comprehensive performance management.


